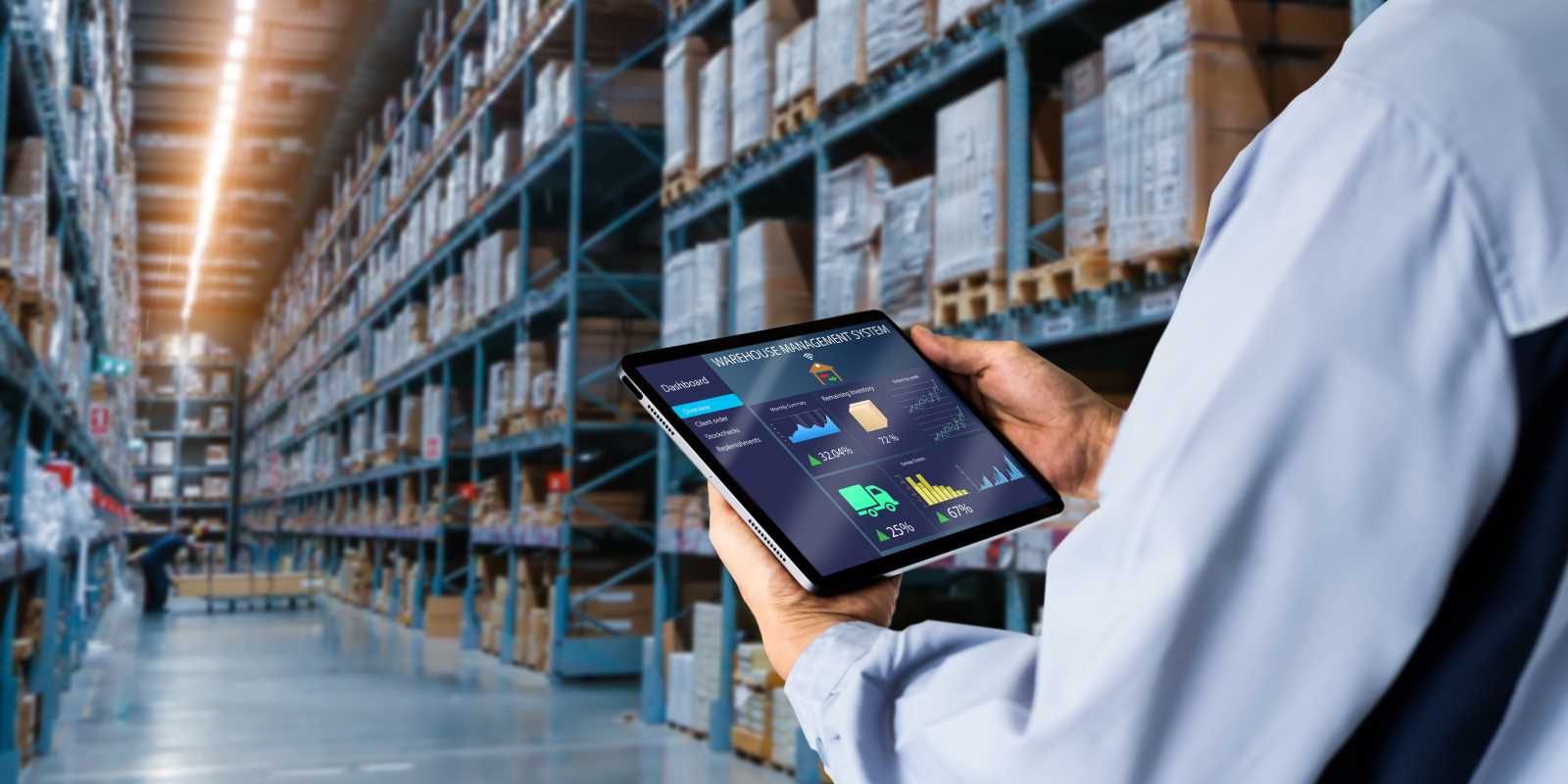
Industries are always on the lookout for ways to boost efficiency and maintain a competitive edge. Edge computing emerges as a groundbreaking technology in this quest. By processing data closer to its source, industries can respond more quickly and improve overall performance. This shift not only accelerates decision-making processes but also transforms how industrial operations function. Edge computing stands at the forefront of innovation, reshaping the industrial landscape and offering a glimpse into a future where speed and efficiency go hand in hand. Let's explore the impact of edge computing on modern industrial practices.
Understanding Edge Computing
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data near the source of data generation rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. Imagine a factory floor equipped with numerous sensors monitoring machinery. Instead of sending all the data to a distant server for analysis, edge computing allows the on-site processing of data. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage, leading to quicker decision-making.
For example, consider a smart manufacturing plant where machines communicate in real-time to optimize production. With edge computing, any issues detect and address immediately without waiting for data to travel to and from the cloud. This immediate processing capability proves crucial for maintaining smooth and efficient operations.
Benefits of Edge Computing in Industrial Operations
- Reduced Latency: Immediate data processing leads to faster responses, essential for time-sensitive applications.
- Enhanced Reliability: Local data processing minimizes the risk of downtime caused by network issues.
- Cost Savings: Decreasing reliance on cloud services can lower operational costs.
- Improved Security: Keeping data closer to the source reduces exposure to potential cyber threats.
In real-world industrial scenarios, these benefits translate to smoother operations and increased productivity. For instance, in a manufacturing setting, reduced latency allows for real-time monitoring and quick adjustments to machinery, preventing costly downtime. Enhanced reliability ensures that production lines continue to run efficiently even if a network disruption occurs. Cost savings arise from minimizing data transfer to the cloud, while improved security safeguards sensitive industrial data from potential breaches.
Challenges and Solutions
While edge computing offers numerous advantages, it also comes with its set of challenges. Addressing these obstacles proves key to successful implementation.
- Scalability: As the number of edge devices grows, managing and scaling the infrastructure can become complex.
- Security: Ensuring data security at multiple edge locations can be more challenging than centralized systems.
- Integration: Combining edge computing with existing IT and OT systems requires careful planning and execution.
To overcome scalability issues, companies adopt centralized management platforms that streamline the deployment and monitoring of edge devices. Enhancing security involves implementing robust encryption and authentication measures to protect data across all edge nodes. For seamless integration, organizations should invest in middleware solutions that facilitate communication between edge and legacy systems, ensuring compatibility and smooth data flow.
Integration with IoT
Edge computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) are closely intertwined. IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, and processing this data efficiently is where edge computing shines. By analyzing data locally, industries can derive actionable insights in real-time without the delays associated with sending data to the cloud. This synergy enables smarter and more responsive industrial operations, enhancing everything from predictive maintenance to supply chain management, as discussed in the context of edge computing.
The Future of Edge Computing in Industry
The future of edge computing in industrial operations looks promising, with several trends and advancements on the horizon. As technology evolves, we can expect even greater integration of edge computing with artificial intelligence and machine learning. This combination enables more sophisticated data analysis and automation, driving further efficiencies and innovations in industrial processes.
Advancements in hardware will make edge devices more powerful and energy-efficient, allowing for broader adoption across various industrial sectors. The development of standardized protocols and frameworks will also facilitate easier implementation and interoperability between different edge solutions. These advancements will solidify edge computing’s role as a cornerstone of modern industrial operations, paving the way for smarter and more resilient industries.
Edge computing is reshaping industrial operations by boosting speed, reliability, and efficiency, making it a key driver of future innovation.
 (Image via
(Image via