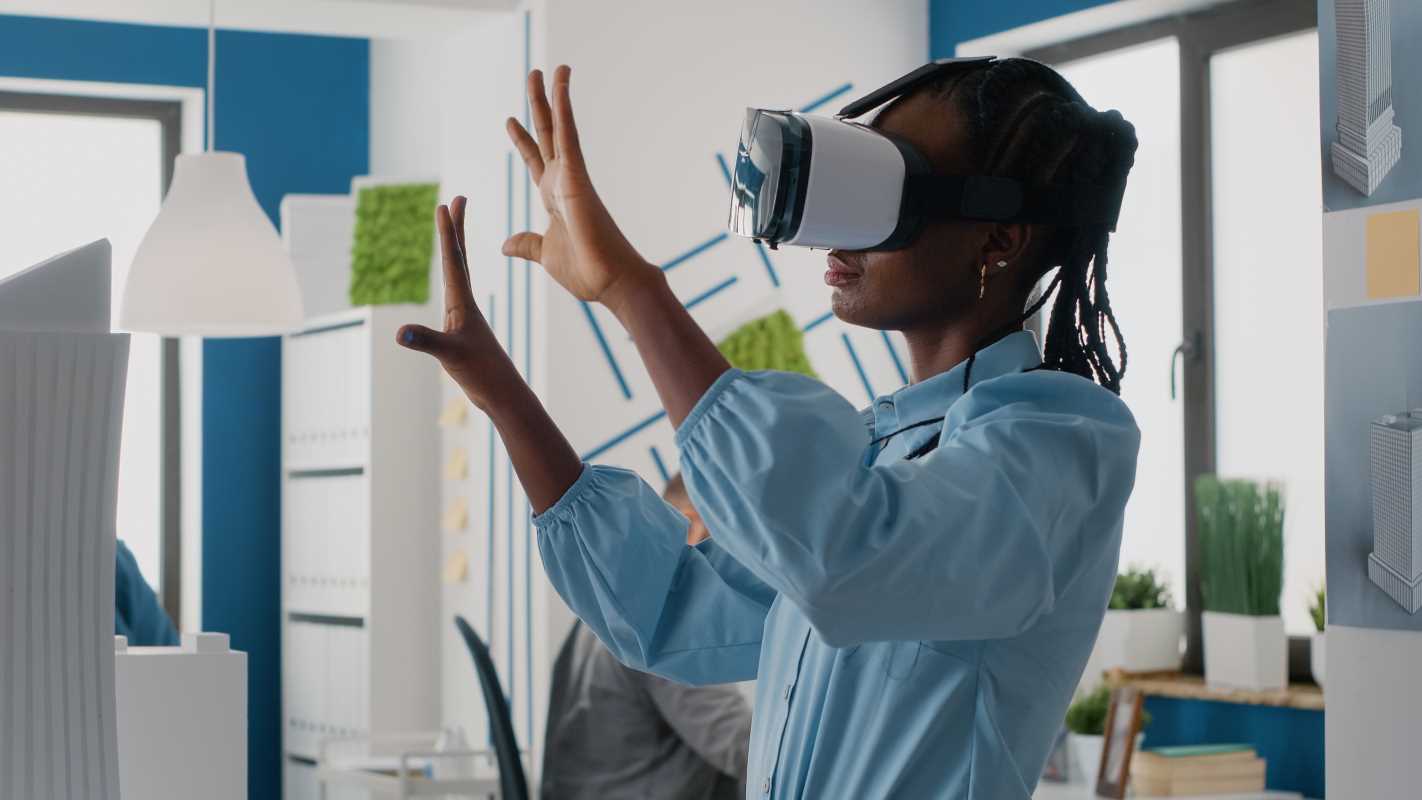
Teams often struggle to connect when meetings take place over standard video calls, with faces lined up in small boxes. Augmented reality changes the way groups work together by placing digital content directly into the physical world. Colleagues can gather around a virtual prototype, manipulate 3D models, or review live data together, even from different locations. During a remote inspection, one person can highlight specific components of a machine, while others see the same tagged parts in real time. This use of spatial context brings a sense of presence and interaction that goes far beyond traditional screen sharing and video meetings.
Getting started doesn’t require bulky gear. Modern smartphones and tablets can handle many AR apps, and dedicated glasses are becoming more affordable. By blending real and virtual layers, participants gain a stronger sense of presence. They point, tap, and manipulate objects together, making planning sessions, design reviews, and training feel more natural.
Essential Augmented Reality Tools for Remote Teams
Choosing the right AR tools determines how easily your team adapts. Some platforms focus on hardware, while others excel at software that works across devices. Find solutions that support the devices your team already owns to save time and money during setup.
- Microsoft HoloLens: Provides hands-free interaction and advanced spatial mapping. Suitable for industrial applications but comes with a higher price tag.
- Magic Leap: Offers vivid visuals and a decent field of view. Its software ecosystem continues to grow steadily.
- Spatial: Compatible with smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses. It syncs 3D models and video feeds within a single virtual room.
- Matterport Capture: Creates 3D meshes of real-world spaces. You can upload scans directly into many collaboration apps.
Most of these tools allow users to join sessions using a smartphone app, which lowers the entry barrier. Teams can begin experimenting without purchasing expensive headsets for everyone. Look for easy onboarding and strong customer support to encourage early adoption.
Designing Engaging Shared Workspaces
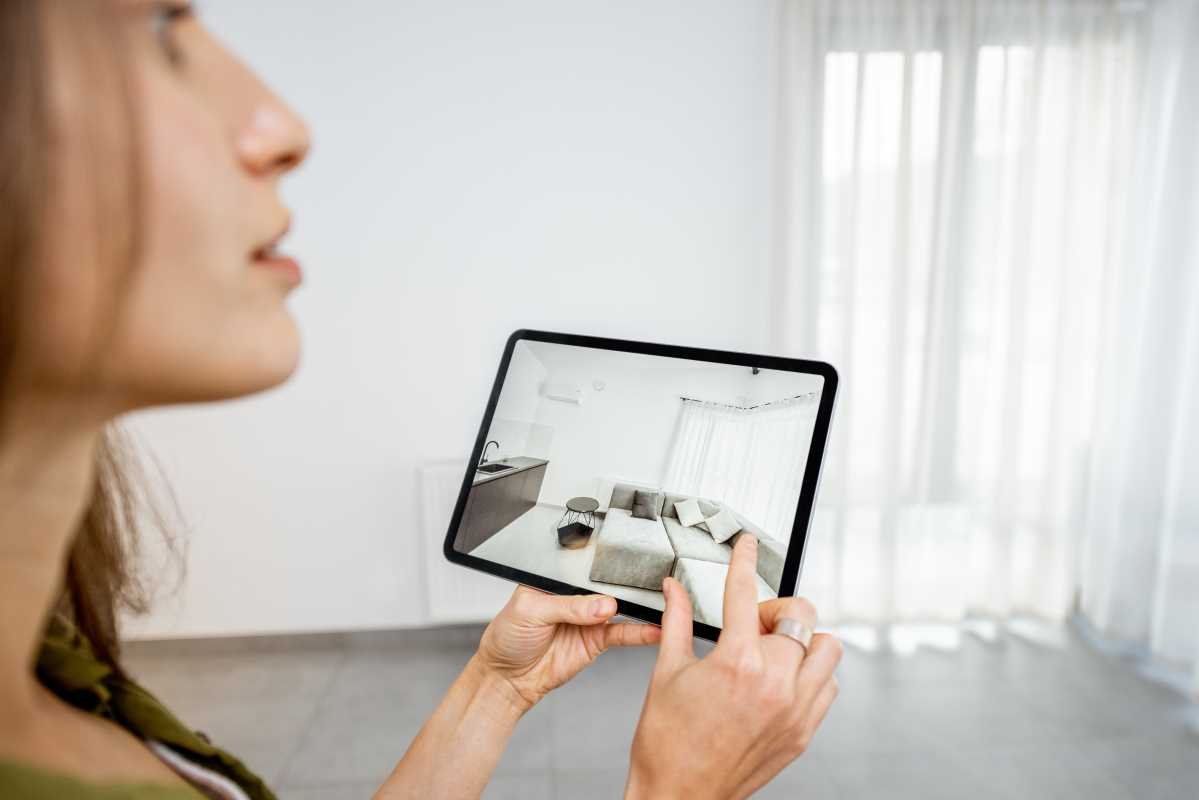
Transform a standard conference call into an immersive experience by setting up carefully. First, create a virtual stage. If you review product designs, load a 3D model in the center of your shared space. Use color-coding to highlight key components or attach notes that hover over critical areas. This visual anchor keeps the session organized and prevents it from becoming a floating jumble of objects.
Encourage each participant to customize their viewpoints. One might zoom into the model’s internals, while another steps back to see the full picture. Motion controls and hand gestures enable users to reposition elements and leave markers. All markers stay visible to everyone, guiding conversations and reducing misunderstandings.
Consider environmental cues as well. When presenting machinery for maintenance training, scan the actual engine room. Insert the digital twin into its real context. Trainees see both the physical space and overlays highlighting valves, wires, or safety zones. This approach reduces guesswork and keeps learners engaged.
Maintain a clutter-free workspace. Regularly delete old annotations and archive completed projects. A clean environment helps new users join without wading through irrelevant items. Use simple color themes and consistent naming conventions to make the environment more intuitive and user-friendly.
Using Live AR Annotations to Enhance Engagement
Annotations allow participants to mark virtual objects, share feedback instantly, and assign tasks visually. When everyone sees the same highlight, teams can quickly move from discussion to action. Point out a design flaw, sketch a fix, or attach a shortcut link to relevant documents.
- Place Notes Directly on Objects: Attach virtual sticky notes to 3D parts. These notes stay anchored so that when someone rotates the model, the comments move with it.
- Draw Freehand Sketches: Use your finger or stylus to scribble arrows, circles, or design ideas over the scene. It feels as natural as using a whiteboard marker, and hands-free options work on headsets too.
- Use Voice Tags for Context: Record short voice clips linked to specific spots in the workspace. Hearing a colleague explain a suggestion adds clarity without long email threads.
- Generate Automated Summaries: After a session, create an overview of all annotations. Assign owners to each task so the team knows who will follow up on next steps.
These real-time interactions keep everyone engaged. Visual cues are easier to remember, and seeing progress unfold motivates deeper participation. You avoid the common “I’ll email that later” problem.
Connecting AR with Collaboration Platforms
AR tools work best when they link to the systems your team already uses. If you depend on project management software or cloud storage, select AR apps that exchange data smoothly. Synchronizing tasks, updating calendars, and linking to design repositories makes transitions seamless.
For example, connect with Slack or Microsoft Teams so AR session invitations appear in your regular chat channels. Embed live AR views into a project wiki or dashboard. Participants can move directly from text discussions into the 3D environment without switching between apps.
Another method involves integrating with IoT sensors or live data feeds. Maintenance crews can wear AR glasses to view real-time performance metrics overlaid on machinery. When an alert triggers in the monitoring system, the AR view displays relevant readings and troubleshooting steps.
APIs and webhooks enable these connections, so plan a data flow diagram before starting. Define which events activate AR updates and how feedback loops send information back to your main platform. Clear integration plans reduce glitches and ensure a smooth experience.
Measuring Results and Gathering User Feedback
Any new technology implementation requires assessment. Track usage statistics, session lengths, and task completion rates. Compare these figures to previous data—did design reviews finish quicker? Did training scores improve? Quantitative data help justify the investment and guide future improvements.
Ask participants for honest feedback. Conduct short surveys after each AR session to identify pain points, desired features, and training obstacles. Inquire about device comfort, interface ease, and meeting effectiveness. Adjust upcoming sessions based on that input.
Hold regular review workshops where team members demonstrate their favorite AR techniques. Peer sharing boosts adoption and sparks new ideas you might not have considered. Highlight success stories to maintain enthusiasm.
If adoption stalls, consider changing your licensing approach. Switch from per-seat plans to usage-based billing or add more headsets for critical teams. Being flexible ensures you support productive users without overspending.
Augmented reality can change remote work from static screens to interactive environments where ideas develop visibly. With the right tools, well-planned workspaces, live annotations, integrated systems, and ongoing feedback, your team can collaborate more naturally and effectively. Hardware improvements and creative efforts will only expand what you can achieve.
Integrate virtual objects into physical spaces to keep everyone engaged. Experiment frequently to make remote meetings more interactive and productive.